Been there
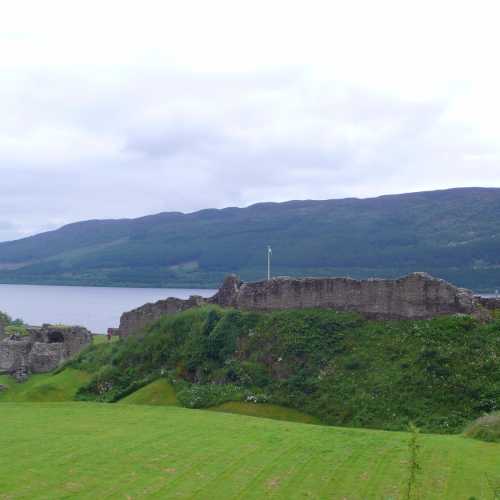
Loch Ness
207995 people visited sight
Loch Ness (/ˌlɒx ˈnɛs/; Scottish Gaelic: Loch Nis [l̪ˠɔx ˈniʃ]) is a large, deep, freshwater loch in the Scottish Highlands extending for approximately 37 kilometres (23 miles) southwest of Inverness. Its surface is 16 metres (52 feet) above sea level. Loch Ness is best known for alleged sightings of the cryptozoological Loch Ness Monster, also known affectionately as «Nessie». It is connected at the southern end by the River Oich and a section of the Caledonian Canal to Loch Oich. At the northern end there is the Bona Narrows which opens out into Loch Dochfour, which feeds the River Ness and a further section of canal to Inverness. It is one of a series of interconnected, murky bodies of water in Scotland; its water visibility is exceptionally low due to a high peat content in the surrounding soil.
Loch Ness is the second largest Scottish loch by surface area at 56 km2 (22 sq mi) after Loch Lomond, but due to its great depth, it is the largest by volume in the British Isles. Its deepest point is 230 m (126 fathoms; 755 ft),[2][3] making it the second deepest loch in Scotland after Loch Morar. A 2016 survey claimed to have discovered a crevice that pushed the depth to 271 m (889 ft) but further research determined it to be a sonar anomaly.[4] It contains more fresh water than all the lakes in England and Wales combined,[3] and is the largest body of water in the Great Glen, which runs from Inverness in the north to Fort William in the south.(WIKI)